Hemo Sampler
What is Hemoflow (HF) Sampler?
The Hemoflow (HF, also known as the Dead End Ultrafiltration) sampler is a large-volume sampling technique that filter the water, capture the pollutants in its cartridge, and release the clean water back to the environment. Once the filtration is completed, the captured pollutant loads are then determined by backwashing elution solution through the cartridge and store in a sample bottle, which is followed by chemical and microbiological assays. The method was originally developed for recovering microbes and viruses from potable water, but it has also been used on riverine flows with variable turbidity levels. The DEUF approach shows the following key advantages for water pollution indicator monitoring: (1) it can filter and concentrate more than hundreds of litres of water, so with a pre-determined flow rate, the sampling process could capture all flows in a day; (2) when the site has very short discharge pulses (potentially highly polluted) with a large volume of baseflow (low pollution level), the DEUF with large-volume filtration could still concentrate sufficient amount of particles or microbes; and (3) the field real-time pollution concentration forms as part of the lab assay processes, which reduce the amount of work and labour required for sample analyses.
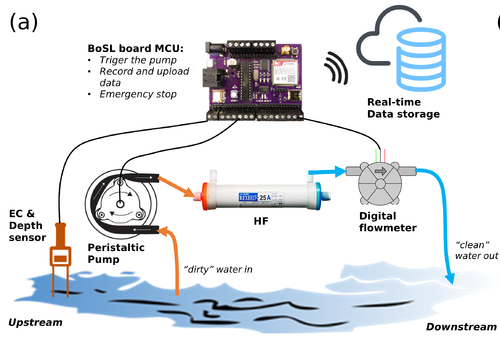
In order to achieve the large-volume sampling in-situ, the HF cartridge and a small peristaltic pumping unit are included in a portable sampler kit, together with our BoSL board, a low-cost water depth, temperature and electrical conductivity (EC) sensor, and a digital flow meter (USN-HS06PA-1, measuring range: 0.1−1.5 L/min). By integrating the low-cost sensor and flow meter into this HF sampler design, we make the sampling processes smarter:
- the pumping process can be automatically turned on and off based on the sensor's readings (i.e., only pump when water is detected)
- the sampling process could be upgraded to flow-based if the flow rate can be estimated
- when the flowmeter detects low flow rates, stop the sampling process to avoid air pressure build-up inside the cartridge
- real-time data communication to record the start and stop time, and the sampling volume
How to quantify the pollution level from the HF
XXX